Last Commit: 2024-01-06 17:50:27
views:
Https
Hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP, which is the primary protocol used to send data between a web browser and a website.
Why we need Https
Http use plain text to transmit data. When we are connecting with a unsecured medium, such as public Wi-Fi, the data can be sniffed by some of software.
It is harmful especially when the data is sensitive, such as password or bank number.
With HTTPS, traffic is encrypted by SSL such that even if the packets are sniffed or otherwise intercepted, they will come across as nonsensical characters.
As the client uses public key to encrypt message, and the server uses private key to decrypt it.
Steps
A Https handshake includes 5 steps as below:
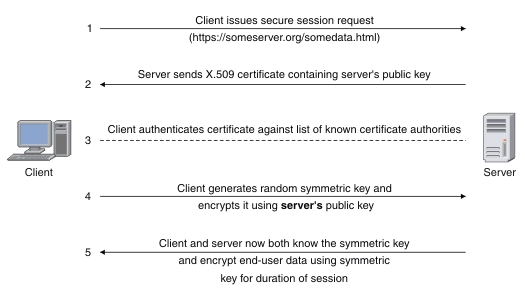
The client sends a request to the server for a secure session. The server responds by sending its X.509 digital certificate to the client.
The client receives the server's X.509 digital certificate.
The client authenticates the server, using a list of known certificate authorities.
The client generates a random symmetric key and encrypts it using server's public key.
The client and server now both know the symmetric key and can use the SSL encryption process to encrypt and decrypt the information contained in the client request and the server response.
So in fact, Https use this symmetric key to encrypt and decrypt data both in the client and the server. As symmetric encryption which is used through the rest is faster and more efficient with large amounts of data transfer. The keys are smaller which is generally why it's faster, but it's algorithm is also easier to process.
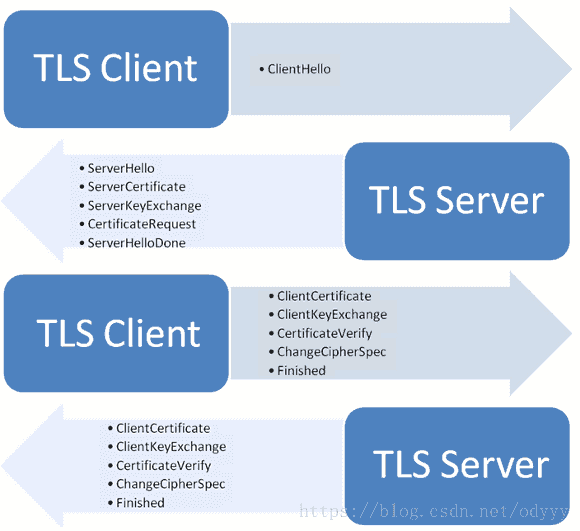
The handshake is as below:
Certificate Validation
As we can see, a Https connection is based on Http connection, the key point it can guarantee security is Certificate. So, how the client to verify a certificate is valid?
Browser downloads the web server's certificate. This certificate is signed with the private key of a trusted certificate (GlobalSign Org) authority.
Browser comes installed with the public keys of all of the major certificate authorities. It uses this public key to verify that the web server's certificate was indeed signed by the trusted certificate authority.
The certificate contains the domain name and/or ip address of the web server. Browser confirms with the certificate authority that the address listed in the certificate is the one to which it has an open connection.
Measure TLS time by curl
When using SSR, the shell as below:
curl -w "TCP handshake: %{time_connect}, SSL handshake: %{time_appconnect}\n" -I --socks5 127.0.0.1:1086 https://www.google.com
use Wireshark to capture TLS connection
- export
SSLKEYLOGFILE
- append
SSLKEYLOGFILEpath to Wireshark
As below:

